Security Overview
This whitepaper describes the different configuration options for data security within Dispatcher Paragon, required configuration and related demands on customer infrastructure.
Communication Paths
Dispatcher Paragon, on very abstract level, is comprised of several network communication paths described in this article. A general overview of the communication is as follows:
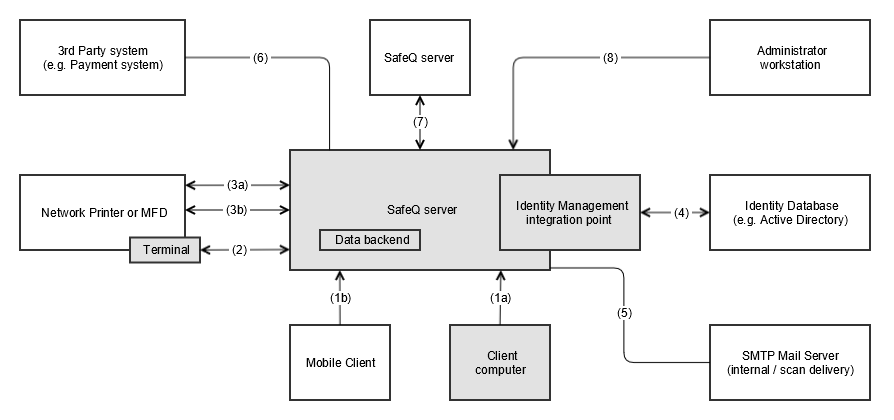
There are eight major paths available in Dispatcher Paragon:
-
Communication from client workstation to SafeQ server – for printing.
-
Sending job from computer
-
Sending job from mobile client
-
-
Communication from terminal/reader to Dispatcher Paragon server – for MFD level authentication
-
Communication from server to network printer / MFD, covering the following:
-
printing
-
AAA services - authentication, authorization and accounting.
-
-
Integration with identity management database or identity / authentication provider or Certification authority.
-
Connection from Dispatcher Paragon server to SMTP mail server or shared network folder for data delivery.
-
Integration with 3rd party applications or systems.
-
Inter-server communication in Distributed SafeQ Server system.
-
Administrator access to Dispatcher Paragon web interface.
Data security options
There are several data transfers realized over the described communication paths. Those data can be secured by following means. Authentication and encryption details will be described further. See Data Encryption Options for additional options.
|
|
Transferred Data |
Unencrypted |
Encrypted |
|
(1a) |
Print from client computer |
HTTP |
TLS (HTTPS) [default] |
|
(1b) |
Print from mobile client |
n/a |
TLS (IPP over SSL) [default] |
|
(2) |
Authentication data from terminal to server |
proprietary or HTTP |
TLS (proprietary or SOAP) [default] |
|
(2) |
Copy / scan session data from terminal to server |
proprietary or HTTP |
TLS (proprietary or SOAP) [default] |
|
(3a) |
Print from server to network printer |
RAW, IPP [default] |
TLS (IPP over SSL) |
|
(3b) |
Scan data delivery from MFD to server |
[default] |
TLS (WebDAV/S) |
|
(4) |
SafeQ integration with identity database provider |
LDAP or JDBC [default] |
TLS (LDAPS) |
|
(5) |
Scan data delivery from server to destinations (mail server, shared network folder) |
IMAP, POP3, SMB [default] |
Protocol dependent |
|
(5) |
Scan data delivery from server to destinations (SharePoint, Dropbox) |
HTTP [default] |
TLS (HTTPS) |
|
(5) |
SafeQ integration with mail server |
SMTP [default] |
TLS 1.0 (SMTPS) |
|
(6) |
SafeQ integration with 3rd party provider |
Provider dependent |
Protocol dependent |
|
(7) |
SafeQ Inter server communication |
Proprietary [default] |
TLS (proprietary) |
|
(8) |
Administrator access to SafeQ web interface |
HTTP |
TLS (HTTPS) |
Internal communication between SafeQ server subsystems is mainly unencrypted by default with optional encryption and authentication. The critical paths are encrypted by default, using the same certificate for all Dispatcher Paragon deployments.
For detailed scheme and information about security of internal communication paths, please refer to Communication paths.
TLS Based Data encryption
Authentication
-
Dispatcher Paragon supports unauthenticated TLS communication for data paths 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8
-
3rd Party communication model is based on individual applications and/or protocols.
-
Server Authentication is enabled by default for data paths:
-
4 (Dispatcher Paragon server verifies LDAP certificate & domain name)
-
7 (SPOC server verifies Management server certificate)
-
8 (Administrator web browser verifies Dispatcher Paragon server certificate & server hostname).
-
-
Server Authentication is supported for data paths:
-
1 (Client computer verifies Dispatcher Paragon server certificate & server hostname. Dispatcher Paragon Client and printer drivers must be installed at the workstation, printer sharing from central server is not possible)
-
2 (Dispatcher Paragon terminal verifies Dispatcher Paragon certificate & server IP address)
-
3a (Dispatcher Paragon server verifies printer certificate & printer hostname)
-
3b (MFD verifies server certificate - this depends on MFD capabilities and requires trusted CA)
-
5 (Dispatcher Paragon server verifies mail server certificate)
-
-
Client authentication is supported for:
-
7 (SPOC server verifies Management server certificate and vice versa)
-
Key management (trusted CA):
-
Administrator uploads trusted issuer (CA) certificate to Dispatcher Paragon.
-
Dispatcher Paragon server certificate(s) - for Terminals, Workstation Clients and administrator workstation(s).
-
Administrator creates certificates for all servers using Trusted CA.
-
Server certificates (private keys) are stored in password protected key store on the Dispatcher Paragon server disk with password hard-coded to the application or in System Key Storage (Windows Certificate Store).
-
Client can verify the server identity using certificate trust and server host name / IP address.
-
-
MFD Certificates
-
MFDs are verified using trusted certificate and hostname.
-
-
LDAP Certificate
-
LDAP server is verified using trusted certificate and hostname.
-
Key management (without trusted CA):
-
Dispatcher Paragon server certificate(s) - for Terminals, Workstation Clients and administrator workstation(s).
-
Administrator creates self-signed certificates for all servers.
-
Server certificates (and private keys) are stored in password protected key store on the Dispatcher Paragon server disk with password hard-coded to the application or in System Key Storage (Windows Certificate Store).
-
Client can verify the server identity using certificate trust and server host name / IP address, in case the created certificate is stored in
-
-
MFD Certificates
-
Dispatcher Paragon retrieves X509 certificate on first connection to the MFD.
-
-
LDAP Certificate
-
Dispatcher Paragon retrieves X509 certificate on first connection to the identity database provider.
-
For detailed guide for setting keys and certificates through all Dispatcher Paragon subsystems see System communication hardening
Authentication
Dispatcher Paragon supports user authentication to the terminal in various modes (Domain username, Username & password, PIN, card and combinations of these). Terminal always communicates authentication data (PIN codes, Card Numbers or User Credentials) via secured TCP/IP communication to Dispatcher Paragon server.
Authentication data are verified by following means:
-
For SPOC - data are ALWAYS verified with Local Data Cache and (only if not found locally) with Management server. Data are replicated to SPOC data caches in scheduled intervals or on demand (by Administrator or 1st User Access).
-
For Management - PIN codes and Card Numbers are verified by sub-string match in Dispatcher Paragon SQL database. PIN codes are typically stored in form of one-way hash.
-
User Credentials (Login/Password) on Management server are verified either by sub-string match in SafeQ SQL database (if manually assigned to the user) or with LDAP - using LDAP/S authentication mechanism. Locally stored passwords (one-way hashes) are replicated to SPOC data cache. If the password is found in SPOC data cache, Management server (and further LDAP server is not used)
Password storage
User passwords stored in Dispatcher Paragon are encoded using a cryptographically secure hash function. A random salt is generated for each password.
Currently the only supported hash function for secure password storage is BCrypt, with configurable strength.
In order to simplify the migration from YSoft SafeQ 5, it is possible, if explicitly enabled, to authenticate against a non-salted MD5 hashed password. In this case, after successful authentication, passwords are rehashed using the standard password encoder and the MD5 hash is removed.
Authorization model
Dispatcher Paragon is managed via a centralized web interface.
It uses Role-based access control (RBAC) with Capability model for certain system operations. The administrator can create multiple roles and delegate selected administrative and managerial permissions and operations to these roles. It is also possible to define personal user accounts with full administrative privileges, and disable the default, anonymous administrative account.
Dispatcher Paragon supports replication of roles from external sources (e.g., Active Directory/LDAPS or CSV file) with additional administration within Dispatcher Paragon.
With Active Directory and eDirectory, the Dispatcher Paragon system takes advantage of advanced Active Directory specific replication information to optimize the replication process.
Impact to system response speed
Enabled encryption of communication paths may produce a delay in data delivery. For most of the communication paths the delay doesn't have any measurable impact to end user experience, most affected data paths are 1, 2 and 3a.
Data delivery throughput for TLS based encryption (SSL over IPP) depends on the speed of the target printer.
Internal System Audit log
SafeQ logs all CRUD operations to log file(s) on the file system using standard Log4j logging library. Manual administrative operations are tracked by the system in dedicated audit logs, which are accessible to delegated users in the web interface.
Passwords and authentication data are not logged. Access to the log files is not controlled and must be managed on operating system level.
Data Storage Methods and Access to the System
All data within the operation of the system is stored in the following ways:
-
Internal SQL database. In case of embedded PGSQL/MSSQL Express, the database is accessible only via the local host interface. In case of an external DB, the security model is the responsibility of the database administrator. The database is accessible only with the name and password stored in the configuration file.
-
Internal Configuration Files. Are stored in the Dispatcher Paragon operation directory in a text format. The data is secured on the same level of access as relevant directories and OS.
-
External Data sources. Configuration dependent.
-
All passwords and user codes are stored in the configuration files and database in an encoded form (one-way hash). Access data to external systems (including access to the SQL DB Dispatcher Paragon itself) is stored encoded by an AES-256 encryption (using hardcoded key).
-
Print job data is stored temporarily on the file system in the plain unencrypted form as received from the source workstation. Using system configuration, this data can be automatically deleted (not wiped) after print or administrator defined expiration time.
Used technologies
The whole solution is proprietary. Java 11 is used for System Core, MS .NET 4.5 Framework for MFD integration and Apache Tomcat, MS SQL or PostgreSQL Database Engines are among standard 3rd party components used in the solution.
Additional notes
Some print drivers support print job data encryption for particular printer. This feature can only be used for direct print to the specified device.
All session timeouts in the system (administrative console or terminal access) are administrator definable using centralized web interface.
There are not practical limitations regarding character sets and length for usernames and passwords. Certain MFDs may impose additional limitations on their own.